New user? / Forgot your password?
0 Item | 0,00 €
Alternariol Monomethyl Ether
Unlock Precision in Residue Analysis with Alternariol Monomethyl Ether
Elevate your laboratorys analytical capabilities with our high-purity reference materials for Alternariol monomethyl ether AME. As a mycotoxin produced by Alternaria fungi, AME is a critical contaminant in food and environmental samples, posing significant health risks. Our meticulously tested reference materials ensure accurate detection and compliance with stringent regulatory standards set by authorities like EFSA and FDA. Trust HPC Standards GmbH for reliable, precise, and high-quality solutions in food and environmental analysis.
Product | Catalog No./ CAS No. | Quantity | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Alternariol monomethyl ether solution | 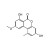 | 685187 | 1X1ML | Please log in. |
D3-Alternariol monomethyl ether solution | 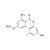 | 684827 | 1X1ML | Please log in. |
High-purity reference materials for precise residue analysis
Overview
Alternariol monomethyl ether (AME) is a mycotoxin produced by several species of the Alternaria fungi. It is commonly found as a contaminant in various crops and food products, posing potential health risks to humans and animals.
Uses
AME is primarily used in scientific research to study its toxicological effects, contamination pathways, and degradation processes. It is also crucial for developing and validating analytical methods for detecting mycotoxins in food and environmental samples.
Regulatory
Regulations concerning AME vary by region, but it is generally subject to strict monitoring due to its potential health risks. Regulatory bodies such as the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) set maximum allowable limits for AME in food products to ensure consumer safety.
Monitoring
Regular monitoring of AME levels in food and environmental samples is essential for compliance with regulatory standards. Laboratories utilize high-purity reference materials to ensure accurate and reliable detection of AME.
Health Impact
AME has been shown to exhibit various toxic effects, including genotoxicity and cytotoxicity. Prolonged exposure to AME can lead to adverse health effects in humans, making it crucial to monitor and control its presence in food products.
Human Toxicity
Studies indicate that AME can cause DNA damage and interfere with cellular processes, leading to potential carcinogenic effects. It is important to limit human exposure to AME to mitigate these health risks.
Environmental Impact
AME can persist in the environment, contaminating soil and water sources. Its presence can adversely affect wildlife and disrupt ecological balance.
Effects on Wildlife
AME exposure can harm wildlife, particularly aquatic organisms, due to its toxic properties. Continuous monitoring and control measures are necessary to protect ecosystems from AME contamination.
Safety Measures
Implementing safety measures such as proper storage, handling, and disposal of AME-containing materials is essential to minimize exposure and environmental impact. Laboratories should follow stringent protocols to ensure safe usage of AME.
Regulation
AME is regulated under various international guidelines to ensure food safety and environmental protection. Compliance with these regulations is mandatory for industries involved in food production and environmental monitoring.
Analytical Standards
High-purity reference materials for AME are essential for accurate residue analysis. These materials help laboratories achieve precise quantification and identification of AME in complex matrices, ensuring reliable results and regulatory compliance.


