New user? / Forgot your password?
0 Item | 0,00 €
Bisphenol A Reference Materials
Ensure Accurate Residue Analysis with High-Purity Bisphenol A Reference Materials
Our high-purity Bisphenol A BPA reference materials are essential for laboratories conducting food and environmental analysis. Tested to meet international quality requirements, these materials ensure compliance with regulatory limits, providing the accuracy and reliability needed for precise residue analysis. Partner with HPC Standards GmbH for top-tier analytical standards in BPA monitoring.
Product | Catalog No./ CAS No. | Quantity | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
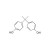 | 674645 | 1X500MG | Please log in. | |
Bisphenol A solution | 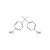 | 677476 | 1X1ML | Please log in. |
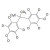 | 675927 | 1X50MG | Please log in. | |
D16-Bisphenol A solution | 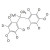 | 689546 | 1X5ML | Please log in. |
High-purity reference materials for accurate and reliable residue analysis of Bisphenol A (BPA).
Overview
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical compound primarily used in the manufacturing of various plastics. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in most common organic solvents but has very poor solubility in water. BPA is produced on an industrial scale by the condensation reaction of phenol and acetone.
Our high-purity reference materials for BPA are tested according to international quality requirements and meet the highest industrial standards. These reference materials are essential for laboratories conducting food and environmental analysis to ensure compliance with regulatory limits.
Uses
BPA's largest single application is as a co-monomer in the production of polycarbonates, which accounts for 65–70% of all BPA production. The manufacturing of epoxy resins and vinyl ester resins account for 25–30% of BPA use. The remaining 5% is used as a major component of several high-performance plastics and as a minor additive in PVC, polyurethane, thermal paper, and several other materials.
Regulatory
The health effects of BPA have been the subject of prolonged public and scientific debate. BPA is a xenoestrogen, exhibiting hormone-like properties that mimic the effects of estrogen in the body. Public health agencies in many countries, as well as the World Health Organization, have investigated BPA. While normal exposure is below the level currently associated with risk, several jurisdictions have taken steps to reduce exposure on a precautionary basis, particularly by banning BPA from baby bottles.
Monitoring
Exposure to BPA is common due to its presence in many everyday materials. Monitoring BPA levels in food and the environment is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance with regulatory standards. Our reference materials provide the accuracy and reliability needed for such monitoring activities.
Health Impact
Human Toxicity
BPA has been found to interact with a diverse range of hormone receptors in both humans and animals. It binds to both of the nuclear estrogen receptors, ERα and ERβ, and can mimic or antagonize estrogen. BPA exhibits very low acute toxicity, with an LD50 of 4 g/kg (mouse). However, its long-term, low-dose exposure effects are still a subject of scientific investigation.
Environmental Impact
Effects on Wildlife
BPA is an environmental contaminant of emerging concern. Despite its short half-life and non-bioaccumulating character, continuous release into the environment causes continuous exposure to both plant and animal life. It affects development and reproduction in a wide range of wildlife, with certain species being particularly sensitive.
Safety Measures
Handling BPA requires adherence to safety guidelines to minimize exposure. Precautionary statements include P201, P202, P261, P273, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P333+P313, P363, and P403+P233.
Analytical Standards
Our high-purity reference materials for BPA are essential for laboratories conducting food and environmental analysis. These materials ensure accurate and reliable residue analysis, helping laboratories comply with regulatory limits and maintain high standards of safety and quality.


