New user? / Forgot your password?
0 Item | 0,00 €
Clothianidin
Clothianidin PREMIUM High-Purity Reference Materials for Precise Residue Analysis
Ensure your laboratorys accuracy and reliability with HPC Standards GmbHs high-purity reference materials for Clothianidin. Our products are rigorously tested to meet international quality requirements and the highest industrial standards, making them essential for food and environmental analysis. Trust HPC Standards GmbH to help you maintain compliance with regulatory limits and achieve unparalleled precision in your residue analysis.
Product | Catalog No./ CAS No. | Quantity | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Clothianidin solution | 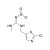 | 673238 | 1X10ML | Please log in. |
Clothianidin solution | 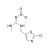 | 673239 | 1X5ML | Please log in. |
ISO 17034 Reference Material | 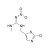 | 674576 | 1X100MG | Please log in. |
ISO 17034 Certified Reference Material | 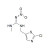 | 692070 | 1X50MG | Please log in. |
D3-Clothianidin solution | 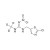 | 679002 | 1X1ML | Please log in. |
Clothianidin: High-Purity Reference Materials for Accurate Residue Analysis
Overview
Clothianidin is an insecticide developed by Takeda Chemical Industries and Bayer AG. It belongs to the neonicotinoid class, which are chemically similar to nicotine. Clothianidin acts on the central nervous system of insects, functioning as an agonist of nAChR, the same receptor as acetylcholine. It is designed to be more stable and longer-lasting than nicotine, making it effective for agricultural use.
Uses
Clothianidin is used in various forms, including spray, dust, soil drench, injectable liquid, and seed treatment. It protects plants against a wide range of agricultural pests and is authorized for use in many countries, including the United States, Canada, and several European nations. It is particularly effective in preventing insect pests from developing resistance to other classes of pesticides like organophosphates and pyrethroids.
Regulatory
Clothianidin has been subject to various regulatory reviews and restrictions. In the European Union, it has been banned for all outdoor uses since 2018 due to its risk to bees. In the United States, it has conditional approval and is widely used. Regulatory authorities emphasize that when used according to label instructions, clothianidin residues on food are not expected to exceed safe levels.
Monitoring
Monitoring of clothianidin involves assessing its environmental persistence, potential for groundwater contamination, and its effects on non-target species like bees and aquatic life. Regulatory agencies require extensive data from manufacturers to ensure that clothianidin does not pose unacceptable risks to the environment and human health.
Health Impact
Clothianidin is moderately toxic to mammals when ingested in large quantities. It poses lower risks to humans compared to organophosphates and carbamates. Laboratory tests indicate that it is not a carcinogen and does not damage genetic material. However, long-term ingestion may result in reproductive and developmental effects.
Environmental Impact
Clothianidin is highly toxic to bees and other pollinators, leading to concerns about its role in colony collapse disorder (CCD). It is also toxic to aquatic invertebrates and has the potential to contaminate groundwater due to its persistence and mobility in the environment. Regulatory measures include buffer zones and restrictions on use during windy conditions to mitigate these risks.
Safety Measure
Safety measures for using clothianidin include personal protective equipment for workers, such as gloves, long-sleeve shirts, and face masks. Users are also required to monitor weather conditions and avoid application during windy days or when rain is forecast. Proper disposal of waste and treated seeds is essential to prevent environmental contamination.
Analytical Standards
HPC Standards GmbH provides high-purity reference materials for clothianidin, ensuring accurate and reliable residue analysis. Our products meet international quality requirements and the highest industrial standards. These reference materials are essential for laboratories conducting food and environmental analysis to ensure compliance with regulatory limits.


