New user? / Forgot your password?
0 Item | 0,00 €
PCB 116 Reference Materials
Ensure Accurate Residue Analysis with High-Purity PCB 116 Reference Materials
Unlock precision in your laboratorys residue analysis with our high-purity PCB 116 reference materials. Essential for food and environmental testing, our standards meet the highest international quality requirements, ensuring compliance with regulatory limits and supporting effective pollution control measures. Trust HPC Standards GmbH for reliable and accurate analytical results.
Product | Catalog No./ CAS No. | Quantity | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
D5-PCB 116 solution | 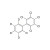 | 676425 | 1X1ML | Please log in. |
D5-PCB 116 solution | 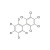 | 677813 | 1X1ML | Please log in. |
PCB 116 solution | 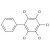 | 692033 | 1X5ML |
High-purity reference materials for accurate and reliable residue analysis of PCB 116.
Overview
PCB 116 (2,3,4,5,6-Pentachlorobiphenyl) is a type of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB), a group of synthetic organic chemicals with 1 to 10 chlorine atoms attached to biphenyl. PCBs have been used in various industrial applications due to their non-flammability, chemical stability, and insulating properties.
Uses
PCBs, including PCB 116, were used in electrical equipment, such as transformers and capacitors, as well as in hydraulic fluids, plasticizers, and other applications. Their production has been banned or restricted in many countries due to their environmental and health impacts.
Regulatory
PCBs are regulated under various national and international frameworks due to their persistence in the environment and potential health risks. Regulations often set limits on PCB concentrations in various matrices, including food, soil, and water.
Monitoring
Monitoring PCB levels is crucial for ensuring compliance with regulatory limits and for assessing the effectiveness of pollution control measures. Analytical methods such as gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS) are commonly used for detecting and quantifying PCB residues.
Health Impact
PCBs, including PCB 116, are known to have various adverse health effects. They can accumulate in the human body and have been associated with several health issues.
Human Toxicity
Exposure to PCBs can lead to skin conditions such as chloracne, as well as liver damage, and may have carcinogenic effects. Chronic exposure is linked to developmental and neurological effects, particularly in children.
Environmental Impact
PCBs are persistent organic pollutants (POPs) that can remain in the environment for long periods, bioaccumulating in wildlife and humans.
Effects on Wildlife
PCBs can affect wildlife, particularly aquatic organisms, leading to reproductive, immunological, and developmental issues. They can also biomagnify through the food chain, impacting higher trophic levels.
Safety Measure
Handling PCBs requires strict safety measures to prevent exposure and environmental contamination. Personal protective equipment (PPE) and proper disposal methods are essential for safe handling.
Regulation
International treaties such as the Stockholm Convention aim to eliminate or restrict the production and use of PCBs. National regulations also set specific limits and guidelines for handling, disposal, and remediation of PCB-contaminated sites.
Analytical Standards
High-purity reference materials for PCB 116 are essential for laboratories conducting residue analysis. These materials ensure the accuracy and reliability of analytical results, supporting regulatory compliance and environmental monitoring efforts.


