New user? / Forgot your password?
0 Item | 0,00 €
Product groups
- A
- Abamectin
- Abscisic acid
- Acenaphthene
- Acenaphthylene
- Acephate
- Acequinocyl
- Acequinocyl-hydroxy
- Acesulfame K
- Acetaldehyde-2,4-DNPH
- Acetamidoantipyrine
- Acetaminophen
- Acetamiprid
- Acetamiprid-N-desmethyl
- Acetochlor
- Acetochlor ESA sodium salt
- Acetochlor OA
- Acetochlor SAA
- Acetone
- Acetyl glyphosate
- Acetyldeoxynivalenol
- Acetylsalicylic acid
- Acetylsulfamethoxazole
- Acibenzolar-S-methyl
- Acifluorfen
- Aclonifen
- Acrinathrin
- Acrolein-2,4-DNPH
- Acrylamide
- Afidopyropen
- AHMI (Phantolide)
- AHTN (Tonalid)
- Alachlor
- Alachlor ESA sodium salt
- Alachlor OA
- Albendazole
- Albendazole sulfoxide
- Albendazole-2-aminosulfone hydrochloride
- Aldicarb
- Aldicarb-sulfone
- Aldicarb-sulfoxide
- Aldrin
- Allethrin
- Alodane
- Altenuene
- Alternariol
- Alternariol monomethyl ether
- Ametoctradin
- Ametryn
- Amidithion
- Amidosulfuron
- Amino-6-chloro-1,3-benzenedisulfonamide
- Aminobiphenyl
- Aminocarb
- Aminoflubendazole
- Aminophenol
- Aminopyralid
- Aminopyridine
- Amisulbrom
- Amitraz
- Amitriptyline hydrochloride
- Amitrole
- AMOZ
- AMPA
- AMPPA
- Anilazine
- Aniline
- Anisidine
- Anthracene
- Anthraquinone
- Antipyrine
- Arprinocid
- Aspon
- Asulam
- Atenolol
- Atranol
- Atrazin
- Atrazine
- Atrazine-2-hydroxy
- Atrazine-desethyl
- Atrazine-desethyl-desisopropyl
- Atrazine-desisopropyl
- Atrazine-desisopropyl-2-hydroxy
- Atropine
- Avermectin B1a
- Avermectin B1b
- Avobenzone
- Azaconazole
- Azadirachtin A
- Azamethiphos
- Azaperol
- Azinphos-ethyl
- Azinphos-methyl
- Aziprotryne
- Azocyclotin
- Azoxystrobin
- Azoxystrobin (free acid)
- Azoxystrobin Metabolite R401553
- Azoxystrobin Metabolite R402173
- Azoxystrobin R230310
- B
- Bambuterol hydrochloride
- Baquiloprim
- Barban
- Beflubutamid
- Benalaxyl
- Bendiocarb
- Benfluralin
- Benfuracarb
- Benfuresate
- Benoxacor
- Bensulfuron-methyl
- Bensulide
- Bentazone
- Bentazone-6-hydroxy
- Bentazone-8-hydroxy
- Benthiavalicarb-isopropyl
- Benzaldehyde
- Benzene
- Benzidine
- Benzobicyclon
- Benzofenap
- Benzoic acid
- Benzophenone
- Benzotriazole
- Benzovindiflupyr
- Benzoximate
- Benzoylprop-ethyl
- Benzo[a]pyrene
- Benzo[b]fluoranthene
- Benzo[c]fluorene
- Benzo[e]pyrene
- Benzo[g,h,i]perylene
- Benzo[j]fluoranthene
- Benzo[k]fluoranthene
- Benzthiazuron
- Benzyl butyl phthalate
- Benzylalcohol
- Benzylaminopurine
- Benzyldimethyldecylammonium chloride
- Benzyldimethyldodecylammonium chloride
- Benzyldimethylhexadecylammonium chloride
- Benzyldimethyloctadecylammonium chloride
- Benz[a]anthracene
- Bezafibrate
- Bicyclopyrone
- Bifenazate
- Bifenazate-diazene
- Bifenox
- Bifenthrin
- Binapacryl
- Biphenyl
- Bis(2-ethylhexyl) adipate
- Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate
- Bis(methylglycol) phthalate
- Bis-palmitoyl-3-chloropropanediol
- Bisphenol A
- Bisphenol S
- Bitertanol
- Bixafen
- Boldenone
- Boscalid (Nicobifen)
- Boscalid Metabolite M510F01
- Brodifacoum
- Broflanilide
- Bromacil
- Bromadiolone
- Brombuterol hydrochloride
- Bromfenvinphos-ethyl
- Bromoacetic acid
- Bromoaniline
- Bromocyclen
- Bromofluorobenzene
- Bromoform
- Bromophenylurea
- Bromophos-ethyl
- Bromophos-methyl
- Bromopropylate
- Bromoxynil
- Bromoxynil-methyl ether
- Bromoxynil-octanoate
- Bromuconazole
- Bufencarb
- Bupirimate
- Buprofezin
- Butachlor
- Butafenacil
- Butamifos
- Butanol
- Butocarboxim
- Butocarboxim-sulfoxide
- Butoxycarboxim
- Butralin
- Buturon
- Butyl Ethyl Ether
- Butyl methyl ether
- Butyl phenyl ether
- Butylate
- Butylated hydroxyanisole
- Butylbenzene
- Butylparaben
- Butylphenol
- C
- Cadusafos
- Caffeine
- Cambendazole
- Camphechlor (Toxaphene)
- Camphor
- Cannabidiolic acid
- Captafol
- Captan
- Carazolol
- Carbamazepine
- Carbamazepine 10,11-epoxide
- Carbaryl
- Carbendazim
- Carbetamide
- Carbofuran
- Carbofuran-3-hydroxy
- Carbofuran-3-keto
- Carbon disulfide
- Carbophenothion
- Carbophenothion-methyl
- Carbophenothion-methyl-sulfone
- Carbosulfan
- Carboxin
- Carboxin-sulfoxide
- Carbuterol acetate hydrate
- Carfentrazone (free acid)
- Carfentrazone-ethyl
- Carnidazole
- Carpropamid
- CDPOS
- Cephacetrile
- Chinomethionat
- Chloramphenicol
- Chlorantraniliprole
- Chlorbenside
- Chlorbenside-sulfone
- Chlorbromuron
- Chlorbufam
- Chlordane
- Chlordecone (Kepone)
- Chlordecone alcohol
- Chlordimeform
- Chlorethoxyfos
- Chlorfenapyr
- Chlorfenprop-methyl
- Chlorfenson
- Chlorfenvinphos
- Chlorfluazuron
- Chlorflurenol-methyl ester
- Chloridazon
- Chloridazon-desphenyl
- Chloridazon-methyl-desphenyl
- Chlorimuron-ethyl
- Chlormadinone acetate
- Chlormephos
- Chlormequat chloride
- Chloro-1,2-propanediol
- Chloro-2-methylaniline
- Chloro-2-nitroaniline
- Chloro-3-methylphenol
- Chloroacetic Acid
- Chloroaniline
- Chloroatranol
- Chlorobenzene
- Chlorobenzilate
- Chlorobenzoic acid
- Chlorobenzuron
- Chlorobutane
- Chloroethanol
- Chloroethyl linoleate
- Chloroethyl oleate
- Chloronaphthalene
- Chloroneb
- Chloronicotinic acid
- Chloronitrobenzene
- Chlorophacinone
- Chlorophenol
- Chlorophenoxyacetic acid
- Chloropropylate
- Chlorothalonil
- Chlorothalonil-4-hydroxy
- Chlorotoluene
- Chlorotoluron
- Chlorotoluron-desmethyl
- Chloroxuron
- Chlorpromazine hydrochloride
- Chlorpropham
- Chlorpyrifos
- Chlorpyrifos-methyl
- Chlorpyrifos-methyl-desmethyl TMA salt
- Chlorsulfuron
- Chlortetracycline hydrochloride
- Chlorthal-dimethyl
- Chlorthalidone
- Chlorthiamid
- Chlorthion
- Chlorthiophos
- Chlozolinate
- Cholecalciferol
- Chromafenozide
- Chrysene
- Cimaterol
- Cimbuterol
- Cinidon-ethyl
- Cinmethylin
- Cinosulfuron
- Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride hydrate
- Citronellol
- Clenbuterol hydrochloride
- Clenpenterol hydrochloride
- Clenproperol
- Clethodim
- Clethodim-sulfone
- Climbazole
- Clindamycin hydrochloride
- Clodinafop (free acid)
- Clodinafop-propargyl
- Clofentezine
- Clofibrate
- Clofibric acid
- Clomazone
- Clomeprop
- Clopyralid
- Cloquintocet-mexyl
- Closantel
- Clothianidin
- Clotrimazole
- Clozapine
- Colchicin
- Cotinine
- Coumachlor
- Coumaphos
- Coumarin
- Crimidine
- Crotoxyphos
- Cyanazine
- Cyanofenphos
- Cyanophos
- Cyantraniliprole
- Cyanuric acid
- Cyazofamid
- Cyclanilide
- Cyclaniliprole
- Cycloate
- Cyclopenta[c,d]pyrene
- Cycloxydim
- Cycloxydim Metabolite BH 517-TGSO2
- Cycluron
- Cyflufenamid
- Cyflumetofen
- Cyfluthrin
- Cyhalofop-butyl
- Cyhalothrin
- Cyhexatin
- Cymiazole
- Cymoxanil
- Cypermethrin
- Cyphenothrin
- Cyproconazole
- Cyprodinil
- Cyprosulfamide
- Cyromazine
- D
- D methyl ester
- D5-Glycidyl palmitate
- Daimuron
- Dalapon
- Dazomet
- DB
- DB-methyl ester
- DDD
- DDE
- DDT
- Decane
- Decanol
- DEET
- Deltamethrin
- Demeton-O
- Demeton-S
- Demeton-S-methyl
- Demeton-S-methyl-sulfone
- Demeton-S-methyl-sulfoxide
- Deoxynivalenol
- Desmedipham
- Desmetryn
- Desoxy-Mequindox
- Desoxycarbadox
- Di-n-octyl phthalate
- Di-n-propyltin dichloride
- Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol
- Di-tert-butylphenol
- Diacetylbenzene
- Diafenthiuron
- Dialifos
- Diallate
- Diaminoanisole
- Diaminotoluene
- Diazinon
- Dibenzo[a,e]pyrene
- Dibenzo[a,h]pyrene
- Dibenzo[a,i]pyrene
- Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene
- Dibenz[a,h]anthracene
- Dibromobenzophenone
- Dibromophenol
- Dibutyl phthalate
- Dicamba
- Dicamba-desmethyl
- Dicamba-methyl ester
- Dichlobenil
- Dichlofenthion
- Dichlofluanid
- Dichlone
- Dichlormid
- Dichloroacetic acid
- Dichloroaniline
- Dichlorobenzamide
- Dichlorobenzene
- Dichlorobenzidine
- Dichlorobenzoic Acid
- Dichlorobenzophenone
- Dichlorobenzyl chloride
- Dichloroethane
- Dichloroethene
- Dichloroisoeverninic acid
- Dichloronitrobenzene
- Dichlorophenol
- Dichlorophenyl)-3-methylurea
- Dichlorophenyl)urea
- Dichloropropan-2-ol
- Dichloropropane
- Dichlorotoluene
- Dichlorovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid
- Dichlorprop
- Dichlorprop-P
- Dichlorvos
- Diclobutrazol
- Diclofenac sodium
- Diclofop (free acid)
- Diclofop-methyl
- Dicloran
- Dicofol
- Dicrotophos
- Dicyandiamide
- Dicyclanil
- Dicyclohexyl phthalate
- Dieldrin
- Diethanolamine
- Diethofencarb
- Diethyl phthalate
- Diethylbenzene
- Diethylene glycol dimethyl ether
- Diethylstilbestrol (mixture of Isomers)
- Difenacoum
- Difenoconazole
- Difenoxuron
- Diflubenzuron
- Diflufenican
- Diflufenzopyr
- Difluoroacetic acid
- Difluorophenylacetic acid
- Dihexyl phthalate
- Dihydroxybenzoic acid
- Dihydroxybenzophenone
- Diisobutyl phthalate
- Diisodecyl phthalate
- Diisononyl phthalate
- Diisopentyl Phthalate
- Diisopropylbenzene
- Dikegulac sodium
- Diltiazem hydrochloride
- Dimefox
- Dimefuron
- Dimethachlor
- Dimethachlor ESA sodium salt
- Dimethachlor Metabolite CGA 369873
- Dimethachlor OA
- Dimethenamid
- Dimethenamid ESA sodium salt
- Dimethenamid OA
- Dimethenamid-P
- Dimethipin
- Dimethoate
- Dimethomorph
- Dimethoxybenzoic acid
- Dimethyl fumarate
- Dimethyl phthalate
- Dimethylaniline
- Dimethyldioctadecylammonium chloride
- Dimethylformamide
- Dimethylnaphthalene
- Dimethylpentane
- Dimethylphenol
- Dimethylphenyl)formamide
- Dimethylphenyl-N-methylformamidine HCl
- Dimethylsulfamide
- Dimethylvinphos
- Dimetilan
- Dimetridazole
- Dimetridazole-2-hydroxy
- Dimoxystrobin
- Diniconazole
- Dinitolmide
- Dinitrobenzene
- Dinitrophenol
- Dinitrosalicylic acid
- Dinitrotoluene
- Dinobuton
- Dinocap
- Dinoseb
- Dinotefuran
- Dinoterb
- Dioxacarb
- Dioxane
- Dioxathion
- Diphenamid
- Diphenylamine
- Dipropetryn
- Dipropyl phthalate
- Diquat dibromide
- Diquat dibromide monohydrate
- Disulfoton
- Disulfoton-sulfone
- Disulfoton-sulfoxide
- Ditalimfos
- Dithianon
- Dithiopyr
- Diuron
- DMSA
- DMST
- DNOC
- Dodemorph
- Dodine
- DPOSA
- E
- Edifenphos
- Eicosane
- Emamectin B1a
- Emamectin B1b
- Emamectin benzoate
- Endosulfan
- Endosulfan-sulfate
- Endrin
- Endrin ketone
- Epichlorohydrin
- Epichlortetracycline hydrochloride
- EPN
- Epoxiconazole
- EPTC
- Ergocalciferol
- Erlose
- Erythromycin
- Esfenvalerate
- Estradiol
- Estrone
- Etaconazole
- Ethalfluralin
- Ethanol
- Ethanolamine
- Ethephon
- Ethidimuron
- Ethiofencarb
- Ethiofencarb-sulfone
- Ethiofencarb-sulfoxide
- Ethion
- Ethiprole
- Ethirimol
- Ethofumesate
- Ethofumesate-2-keto
- Ethoprophos
- Ethoxyquin
- Ethoxyquin Dimer
- Ethyl-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)perfluorooctylsulfonamide
- Ethylaniline
- Ethylbenzene
- Ethylene thiourea
- Ethylguaiacol
- Ethylisopropylnitrosamine
- Ethylparaben
- Ethylphenol
- Ethyltoluene
- Ethynylestradiol
- Etofenprox
- Etoxazole
- Etridiazole
- Etrimfos
- Eugenol
- F
- Famoxadone
- Famphur
- Febantel
- Fenamidone
- Fenamiphos
- Fenamiphos-sulfone
- Fenamiphos-sulfoxide
- Fenarimol
- Fenazaquin
- Fenbendazole
- Fenbuconazole
- Fenbutatin oxide
- Fenchlorazole-ethyl
- Fenchlorphos
- Fenchlorphos-oxon
- Fenfluthrin
- Fenfuram
- Fenhexamid
- Fenitrothion
- Fenobucarb
- Fenofibrate
- Fenofibric acid
- Fenoprop
- Fenothiocarb
- Fenoxanil
- Fenoxaprop-P
- Fenoxaprop-P-ethyl
- Fenoxycarb
- Fenpiclonil
- Fenpropathrin
- Fenpropidin
- Fenpropimorph
- Fenpyrazamine
- Fenpyroximate
- Fenson
- Fensulfothion
- Fensulfothion-oxon
- Fensulfothion-oxon-sulfone
- Fensulfothion-sulfone
- Fenthion
- Fenthion-oxon
- Fenthion-oxon-sulfone
- Fenthion-oxon-sulfoxide
- Fenthion-sulfone
- Fenthion-sulfoxide
- Fentin acetate
- Fentin chloride
- Fenuron
- Fenvalerate
- Ferimzone
- Fipronil
- Fipronil-desulfinyl
- Fipronil-sulfide
- Fipronil-sulfone
- Firocoxib
- Flamprop
- Flamprop-methyl
- Flazasulfuron
- Flonicamid
- Florasulam
- Florfenicol amine
- Florpyrauxifen-benzyl
- Fluacrypyrim
- Fluazifop
- Fluazifop-butyl
- Fluazifop-methyl
- Fluazifop-P-butyl
- Fluazinam
- Fluazuron
- Flubendazole
- Flubendiamide
- Flubenzimine
- Fluchloralin
- Flucycloxuron
- Flucythrinate
- Fludioxonil
- Fluensulfone
- Flufenacet
- Flufenacet ESA sodium salt
- Flufenacet Metabolite FOE5043
- Flufenoxuron
- Flufenzine
- Flumequine
- Flumethrin
- Flumetralin
- Flumetsulam
- Flumioxazin
- Flunixin
- Fluometuron
- Fluopicolide
- Fluopyram
- Fluoranthene
- Fluorene
- Fluoroaniline
- Fluoroglycofen-ethyl
- Fluotrimazole
- Fluoxastrobin
- Flupyradifurone
- Flupyrimin
- Flupyrsulfuron-methyl
- Fluquinconazole
- Flurenol-butyl ester
- Flurochloridone
- Fluroxypyr
- Fluroxypyr-1-methylheptylester
- Flurprimidol
- Flurtamone
- Flusilazole
- Fluthiacet-methyl
- Flutianil
- Flutolanil
- Flutriafol
- Fluvalinate
- Fluvoxamine maleate
- Fluxametamide
- Fluxapyroxad
- Folpet
- Fomesafen
- Fonofos
- Foramsulfuron
- Forchlorfenuron
- Formaldehyde-2,4-DNPH
- Formetanate hydrochloride
- Formothion
- Fosetyl-aluminium
- Fosthiazate
- FRD-902
- FRD-903
- Fructose
- Fuberidazole
- Furalaxyl
- Furametpyr
- Furan
- Furathiocarb
- Furazolidone
- Furosemide
- G
- Gabapentin
- Galactosan
- Gemfibrozil
- Genite
- Geraniol
- Glucoheptose
- Glucose
- Glufosinate hydrochloride
- Glufosinate-ammonium
- Glufosinate-N-acetyl
- Glutaraldehyde-DNPH
- Glycidyl palmitate
- Glycidyl Stearate
- Glyphosate
- Glyphosate isopropylamine salt
- H
- Halauxifen (free acid)
- Halauxifen-methyl
- Halfenprox
- Halofenozide
- Halofuginone hydrobromide
- Halosulfuron-methyl
- Haloxyfop
- Haloxyfop-2-ethoxyethyl
- Haloxyfop-methyl
- HCH
- Heptachlor
- Heptachlor-endo-epoxide
- Heptachlor-exo-epoxide
- Heptachlorodecane (CP-8)
- Heptadecanoic acid-methyl ester
- Heptafluorobutyric acid
- Heptenophos
- Heptyltintrichloride
- Hexabromocyclododecane
- Hexachloro-1,3-butadiene
- Hexachlorobenzene
- Hexaconazole
- Hexaflumuron
- Hexazinone
- Hexythiazox
- HHCB (Galaxolide)
- Higenamine hydrochloride
- Homovanillic acid
- Hydramethylnon
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- Hydroprene
- Hydroxy-propoxycarbazone
- Hydroxybenzonitrile
- Hydroxyclomazone
- Hydroxyflunixin
- Hydroxyibuprofen
- Hydroxymebendazole
- Hydroxymethyl)-2-furaldehyd
- Hydroxymethylclenbuterol hydrochloride
- Hydroxyproline
- Hydroxystanozolol
- Hydroxythiabendazole
- I
- Ibuprofen
- Imazalil
- Imazamethabenz (free acid)
- Imazamethabenz-methyl
- Imazamox
- Imazapic
- Imazapyr
- Imazaquin
- Imazethapyr
- Imazosulfuron
- Imibenconazole
- Imidacloprid
- Imidacloprid guanidine hydrochloride
- Imidacloprid olefin
- Indaziflam
- Indeno[1,2,3-c,d]pyrene
- Indoxacarb
- Iodofenphos
- Iodosulfuron-methyl sodium
- Iohexol
- Iopromide
- Ioxynil
- Ioxynil-methyl
- Ioxynil-octanoate
- Ipconazole
- IPPD-Quinone
- Iprobenfos
- Iprodione
- Ipronidazole
- Ipronidazole-hydroxy
- Iprovalicarb
- Irbesartan
- Isazofos
- Isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazine
- Isocarbophos
- Isocycloseram
- Isodrin
- Isofenphos
- Isofenphos-methyl
- Isofenphos-oxon
- Isofetamid
- Isomethiozin
- Isonoruron
- Isoprocarb
- Isopropalin
- Isopropyl-3-methoxypyrazine
- Isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinol
- Isopropylaniline
- Isopropylparaben
- Isoprothiolane
- Isoproturon
- Isopyrazam
- Isoxaben
- Isoxadifen-ethyl
- Isoxaflutole
- Isoxaflutole diketonitrile RPA 202248
- Isoxathion
- Ivermectin
- J
- K
- L
- Labetalol hydrochloride
- Lasalocid A sodium salt
- Lenacil
- Lepimectin
- Leptophos
- Lidocaine
- Limonene
- Linalool
- Linuron
- Lomefloxacin hydrochloride
- Lufenuron
- M
- Mabuterol hydrochloride
- Malaoxon
- Malathion
- Maleic hydrazide
- Malic acid
- Maltotetraose
- Mandestrobin
- Mandipropamid
- Mapenterol hydrochloride
- Matrine
- MCPA
- MCPB
- MCPD sodium sulfate
- Mebendazole
- Mecarbam
- Mecoprop
- Mecoprop-1-octyl ester
- Medroxyprogesterone
- Mefenacet
- Mefenamic acid
- Mefenpyr-diethyl
- Mefentrifluconazole
- Megestrol
- Melamine
- Meloxicam
- Menthol
- Mepanipyrim
- Mepanipyrim-2-hydroxypropyl
- Mepiquat iodide
- Mepivacaine hydrochloride
- Mepronil
- Meptyldinocap
- Mercaptobenzimidazole
- Mesosulfuron-methyl
- Mesotrione
- Metaflumizone
- Metalaxyl
- Metalaxyl Metabolite CGA 108906
- Metalaxyl-M
- Metamitron
- Metazachlor
- Metazachlor ESA
- Metazachlor ESA sodium salt
- Metazachlor Metabolite 479M16
- Metazachlor OA
- Metconazole
- Metformin hydrochloride
- Methabenzthiazuron
- Methacrifos
- Methacrolein-2,4-DNPH
- Methamidophos
- Methanol
- Methidathion
- Methimazole
- Methiocarb
- Methiocarb-sulfone
- Methiocarb-sulfoxide
- Methomyl
- Methoprene
- Methoprotryne
- Methoxyacetophenone
- Methoxychlor
- Methoxyfenozide
- Methoxymethylaniline
- Methyl salicylate
- Methyl-1H-benzotriazole
- Methyl-4-nitroso-piperazine
- Methylchrysen
- Methylchrysene
- Methylhippuric acid
- Methylimidazole
- Methylnaphthalene
- Methylparaben
- Methylpentane
- Methylperfluorooctane sulfonamidoacetic acid
- Methylphenol
- Methylphosphinico)propionic acid
- Methylsulfonyl)-2-nitrobenzoic acid
- Metobromuron
- Metolachlor
- Metolachlor ESA sodium salt
- Metolachlor Metabolite CGA 368208
- Metolachlor Metabolite CGA 37735
- Metolachlor Metabolite NOA 413173
- Metolachlor OA
- Metolcarb
- Metominostrobin
- Metoprolol tartrate
- Metosulam
- Metoxuron
- Metoxuron-monomethyl
- Metrafenone
- Metribuzin
- Metribuzin-desamino
- Metronidazole
- Metronidazole-hydroxy
- Metsulfuron-methyl
- Metyltetraprole
- Mevinphos
- Mexacarbate
- Milbemectin A3
- Milbemectin A4
- Miloxacin
- Mirex
- Molinate
- Monocrotophos
- Monolinuron
- Monononadecanoin
- Monuron
- Morpholine
- Morphothion
- Moxidectin
- Musk ketone
- Musk xylene
- Myclobutanil
- N
- Naled
- Nalidixic acid
- Naphthalene
- Naphthol
- Naphthoxyacetic acid
- Naphthylamine
- Napropamide
- Naproxen
- Naptalam
- Narasin
- Naringenin
- Neburon
- Nicotine
- Nifursol-desfurfuryliden
- Nitenpyram
- Nitralin
- Nitrapyrin
- Nitro-benzaldehydesemicarbazone
- Nitrobenzene
- Nitrofen
- Nitrofurantoin
- Nitrofurazone
- Nitrophenol
- Nitrophenyl a-D-maltohexaoside
- Nitropropane
- Nitroso-di-n-butylamine
- Nitroso-N-methyl-4-aminobutyric acid
- Nitroso-N-methylaniline
- Nitrosobis(2-hydroxyethyl)amine
- Nitrosodibenzylamine
- Nitrosodibutylamine
- Nitrosodiethylamine
- Nitrosodiisobutylamine
- Nitrosodiisopropylamine
- Nitrosodimethylamine
- Nitrosodipropylamine
- Nitrosoethylmethylamine
- Nitrosomorpholine
- Nitrosopiperidine
- Nitrosopyrrolidine
- Nitrothal-isopropyl
- Nitrotoluene
- NMP
- Nonachlor
- Nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonic acid
- Nonafluoropentanoic acid
- Nonylphenol
- Nonylphenol (technical mixture)
- Nonylphenol-di-ethoxylate
- Nonylphenol-mono-ethoxylate
- Norepinephrine hydrochloride
- Norfloxacin
- Norflurazon
- Novaluron
- NP-AHD
- NP-AMOZ
- NP-DNSAH
- Nuarimol
- O
- Ochratoxin A
- Ochratoxin alpha
- Octachlorostyrene
- Octane
- Octanediol
- Octanoic acid 4-cyano-2,6-diiodophenyl ester
- Octanol
- Octocrylene
- Octylphenol
- Octylphenol-di-ethoxylate
- Octylphenol-mono-ethoxylate
- Ofloxacin
- Ofurace
- Oleoyl Ethanolamide
- Omethoate
- Orciprenaline acetate hydrate
- Oryzalin
- Oxadiargyl
- Oxadiazon
- Oxadixyl
- Oxamyl
- Oxamyl-oxime
- Oxasulfuron
- Oxathiapiprolin
- Oxfendazole
- Oxibendazole
- Oxolinic acid
- Oxybenzone
- Oxycarboxin
- Oxyclozanide
- Oxyfluorfen
- Oxytetracycline hydrochloride
- P
- Paclobutrazol
- PAH-Mix 9
- Paraoxon-ethyl
- Paraoxon-methyl
- Paraquat dichloride
- Parathion-ethyl
- Parathion-methyl
- Patulin
- Pazufloxacin mesylate
- PCB 116
- PCB 180
- PCB 209
- PCB 52
- Pebulate
- Penconazole
- Pencycuron
- Pencycuron-PB-amine
- Pendimethalin
- Penflufen
- Penicillin V potassium salt
- Penoxsulam
- Pentachloroaniline
- Pentachloroanisole
- Pentachlorobenzene
- Pentachlorophenol
- Pentachlorothioanisole
- Pentadecafluorooctanoic acid
- Pentaerythrityltetranitrate
- Penthiopyrad
- Pentyl-iso-pentylphthalate
- Perfluorodecanesulfonic acid
- Perfluorohexanesulfonic acid
- Perfluorononanesulfonic acid sodium salt
- Perfluorooctanoic acid
- Perfluorotetradecanoic acid
- Permethrin
- Perthane
- Perylene
- Pethoxamid
- Phenanthrene
- Phenetidine
- Phenkapton
- Phenmedipham
- Phenol
- Phenothrin
- Phenoxyethanol
- Phenthoate
- Phenyl-2-thiouracil
- Phenylacetaldehyde (stabilized)
- Phenylbutazone
- Phenylenediamine
- Phenylethanolamine A
- Phenylphenol
- Phorate
- Phorate-oxon
- Phorate-oxon-sulfone
- Phorate-oxon-sulfoxide
- Phorate-sulfone
- Phorate-sulfoxide
- Phosalone
- Phosfolan
- Phosmet
- Phosmet-oxon
- Phosphamidon
- Phosphonic acid
- Phoxim
- Phthalimide
- Picaridin
- Picloram
- Picolinafen
- Picoline
- Picoxystrobin
- Pinene
- Pinoxaden
- Piperonyl butoxide
- Pirimicarb
- Pirimicarb-desamido-desmethyl
- Pirimicarb-desmethyl
- Pirimicarb-desmethyl-formamido
- Pirimiphos-ethyl
- Pirimiphos-methyl
- Pirimiphos-methyl-desmethyl TMA salt
- Piroxicam
- Plifenate
- Potasan
- PPD
- PPD-quinone
- Prallethrin
- Pretilachlor
- Primidone
- Primisulfuron-methyl
- Prochloraz
- Prochloraz desimidazole-amino BTS44595
- Prochloraz Metabolite BTS40348
- Prochloraz metabolite BTS44596
- Procymidone
- Profenofos
- Profluralin
- Profoxydim lithium salt
- Progesterone
- Promecarb
- Prometon
- Prometryn
- Propachlor
- Propachlor ESA sodium salt
- Propachlor OA
- Propamocarb
- Propamocarb hydrochloride
- Propanil
- Propaquizafop
- Propargite
- Propazine
- Propetamphos
- Propham
- Propiconazole
- Propisochlor
- Propoxur
- Propoxycarbazone sodium
- Propranolol hydrochloride
- Propylene glycol
- Propylene thiourea
- Propylparaben
- Propyltin chloride
- Propyzamide
- Proquinazid
- Prosulfocarb
- Prosulfuron
- Prothioconazole
- Prothioconazole-desthio
- Prothiofos
- Prothoate
- Pydiflumetofen
- Pymetrozine
- Pyracarbolid
- Pyraclofos
- Pyraclostrobin
- Pyraflufen monohydrate (free acid)
- Pyraflufen-ethyl
- Pyrasulfotole
- Pyrazophos
- Pyrazoxyfen
- Pyrene
- Pyrethrins
- Pyribencarb
- Pyridaben
- Pyridafol
- Pyridalyl
- Pyridaphenthion
- Pyridate
- Pyrifenox
- Pyrimethanil
- Pyrimethanil Metabolite M605F002
- Pyrimidifen
- Pyriminobac-methyl
- Pyriofenone
- Pyriproxyfen
- Pyroxasulfone
- Q
- QDI
- Quinalphos
- Quinclorac
- Quinmerac
- Quinoclamine
- Quinoline
- Quinoxyfen
- Quintiofos
- Quintozene
- Quizalofop
- Quizalofop-ethyl
- Quizalofop-P-ethyl
- Quizalofop-p-tefuryl
- R
- S
- S421
- Saccharin
- Saccharose
- Saflufenacil
- Saflufenacil Metabolite M800H11
- Saflufenacil Metabolite M800H35
- Salbutamol acetate
- Salbutamol hemisulfate salt
- Salicylic acid
- Salmeterol xinafoate
- Sarafloxacin hydrochloride
- Scopolamine hydrobromide trihydrate
- Sebuthylazine
- Secbumeton
- Secnidazole
- Sedaxane
- Semduramicin sodium
- Sethoxydim
- Siduron
- Silafluofen
- Silthiofam
- Simazine
- Simazine-2-hydroxy
- Simvastatin
- Sisapronil
- Sodium chlorate
- Sodium cyclamate
- Sodium perchlorate
- Sodium perchlorate monohydrate
- Sorbitol
- Sotalol hydrochloride
- Spinetoram
- Spinosad
- Spinosyn D
- Spirodiclofen
- Spiromesifen
- Spirotetramat
- Spirotetramat-enol-glucoside
- Spirotetramat-keto-hydroxy
- Spirotetramat-mono-hydroxy
- Spiroxamine
- Stanozolol
- Styrene
- Sulcotrione
- Sulfacetamide
- Sulfachloropyridazine
- Sulfadiazine
- Sulfadimethoxine
- Sulfadoxine
- Sulfaguanidine monohydrate
- Sulfamerazine
- Sulfamethazine
- sulfamethizole
- Sulfamethoxazole
- sulfamethoxypyridazine
- Sulfamonomethoxine
- Sulfamoxole
- Sulfanilamide
- Sulfanitran
- Sulfaphenazole
- Sulfapyridine
- Sulfaquinoxaline sodium salt
- Sulfathiazole
- Sulfentrazone
- Sulfisoxazole
- Sulfosulfuron
- Sulfotep
- Sulfoxaflor
- Sulprofos
- Sulprofos-sulfoxide
- Surrogate Mix ISO 27065 and ISO 18889
- Swep
- T
- T-methyl ester
- Taleranol
- TCMTB (Busan)
- Tebuconazole
- Tebuconazole-tert-butyl-hydroxy
- Tebufenozide
- Tebufenpyrad
- Tebupirimfos
- Tebutam
- Tebuthiuron
- Tecnazene
- Teflubenzuron
- Tefluthrin
- Telodrin
- Tembotrione
- Tembotrione metabolite AE 1417268
- Temephos
- Tenuazonic acid mixture of diastereomers
- TEPP
- Tepraloxydim
- Terbacil
- Terbufos
- Terbufos-sulfone
- Terbufos-sulfoxide
- Terbumeton
- Terbumeton-desethyl
- Terbuthylazine
- Terbuthylazine-2-hydroxy
- Terbuthylazine-desethyl
- Terbuthylazine-desethyl-2-hydroxy
- Terbutryn
- Terphenyl
- Terpinene
- Terpineol
- Tetra-n-butyltin
- Tetrachloroanisole
- Tetrachlorobenzene
- Tetrachloroethane
- Tetrachloroethene
- Tetrachlorophenol
- Tetrachlorotoluene
- Tetrachlorvinphos
- Tetraconazole
- Tetradifon
- Tetrahydrophthalimide
- Tetramethrin
- Tetraniliprole
- Tetrasul
- TFNA
- TFNA-AM
- TFNG
- Thenylchlor
- Thiabendazole
- Thiacloprid
- Thiadone (Flufenacet metabolite)
- Thiamethoxam
- Thiamethoxam metabolite CGA 353968
- Thiazafluron
- Thidiazuron
- Thiencarbazone-methyl
- Thifensulfuron-methyl
- Thiobencarb
- Thiodicarb
- Thiofanox
- Thiofanox-sulfone
- Thiofanox-sulfoxide
- Thiometon
- Thionazin
- Thiophanate-ethyl
- Thiophanate-methyl
- Thiram
- Thymol
- Tiocarbazil
- Tolclofos-methyl
- Tolfenamic acid
- Tolfenpyrad
- Toltrazuril sulfone
- Toltrazuril-sulfoxide
- Toluene
- Toluic acid
- Toluidine
- Tolylfluanid
- Topramezone
- Tralkoxydim
- Tralomethrin
- Transfluthrin
- Trenbolone
- Triadimefon
- Triadimenol
- Triallate
- Triamiphos
- Triasulfuron
- Triazamate
- Triazophos
- Triazoxide
- Tribenuron-methyl
- Tribromoanisole
- Tribromophenol
- Tributyl phosphate
- Tributyltin chloride
- Trichlorfon
- Trichloroacetic acid
- Trichloroaniline
- Trichloroanisole
- Trichlorobenzene
- Trichloroethane
- Trichloroethene
- Trichloromethane
- Trichloronate
- Trichlorophenol
- Trichlorophenoxyacetic Acid
- Trichlorotoluene
- Trichodiene
- Triclabendazole
- Triclabendazole-sulfone
- Triclabendazole-sulfoxide
- Triclocarban
- Triclopyr
- Triclosan
- Triclosan-methyl
- Tricyclazole
- Tricyclohexyltin chloride
- Tridemorph (technical mixture)
- Trietazine
- Triethanolamine
- Triethyl phosphate
- Trifloxystrobin
- Triflumizole
- Triflumizole Metabolite FM-1-1
- Triflumizole Metabolite FM-6-1
- Triflumuron
- Trifluoroacetic acid sodium salt
- Trifluorophenylacetic acid
- Trifluralin
- Triflusulfuron-methyl
- Triforine
- Trimethacarb
- Trimethoprim
- Trimethoxyphenylacetic acid
- Trimethylaniline
- Trimethylbenzene
- Trimethylphenol
- Trimethylsulfonium iodide
- Trimetoquinol hydrochloride
- Trinexapac
- Trinexapac-ethyl
- Trinitrotoluene
- Triphenylphosphate
- Triticonazole
- Tritosulfuron
- U
- V
- Valifenalate
- Valsartan
- Vamidothion
- Vamidothion-sulfone
- Vamidothion-sulfoxide
- Vanillin
- Venlafaxine hydrochloride
- Versandkosten
- Vinclozolin
- X
- Z
Ethanolamine Reference Materials
Unlock Precision with High-Purity Ethanolamine Reference Materials
Ensure your laboratorys residue analysis is accurate and reliable with our high-purity Ethanolamine reference materials. Essential for food and environmental analysis, our products meet the highest industrial standards and comply with international quality requirements. Partner with HPC Standards GmbH for unmatched expertise in analytical standards.
Product | Catalog No./ CAS No. | Quantity | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
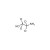 | 687643 | 1X50MG | Please log in. | |
 | 683742 | 1X1ML | Please log in. | |
Ethanolamine solution |  | 687641 | 1X1ML | Please log in. |
High-purity reference materials for accurate and reliable residue analysis.
Overview
Ethanolamine, also known as 2-aminoethanol or monoethanolamine (MEA), is a naturally occurring organic chemical compound with the formula C2H7NO. It is a colorless, viscous liquid with an ammonia-like odor and is both a primary amine and a primary alcohol.
Uses
Ethanolamine is used as a feedstock in the production of detergents, emulsifiers, polishes, pharmaceuticals, corrosion inhibitors, and chemical intermediates. It is also used in gas stream scrubbing to remove carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide from various gas streams. In pharmaceuticals, it is used for buffering or preparation of emulsions, and in cosmetics as a pH regulator.
Regulatory
Regulatory guidelines for ethanolamine are established to ensure safe handling and usage. It is subject to various safety and environmental regulations globally.
Monitoring
Monitoring ethanolamine levels in environmental and food samples is crucial for compliance with regulatory limits. Laboratories require high-purity reference materials to ensure accurate analysis.
Health Impact
Ethanolamine can be toxic to humans if ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin. It can cause irritation to the respiratory tract, skin, and eyes.
Human Toxicity
Exposure to ethanolamine can result in symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath, skin burns, and eye damage. Long-term exposure may lead to more severe health issues.
Environmental Impact
Ethanolamine can have detrimental effects on the environment. It is biodegradable but can be toxic to aquatic life.
Effects on Wildlife
Exposure to ethanolamine can be harmful to wildlife, particularly aquatic organisms, due to its toxicity and potential to cause environmental pollution.
Safety Measures
Proper safety measures should be taken when handling ethanolamine, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and respirators. Adequate ventilation and storage in a cool, dry place are also recommended.
Regulation
Ethanolamine is regulated under various international guidelines to ensure its safe use and handling. Compliance with these regulations is essential for manufacturers and users.
Analytical Standards
High-purity reference materials for ethanolamine are essential for laboratories conducting residue analysis in food and environmental samples. These reference materials ensure accurate and reliable results, meeting the highest industrial standards.


